Vendor audits are the evaluations of your suppliers, contractors, or third-party providers’ compliance to the terms of agreement and other contractual obligations carried out in a systematic way. You can think of it like a quality assurance system for your supply chain or network of service. If your vendors fall short with any of these, the consequences can be severe, attracting costly disruptions, legal penalties, data breaches, or reputational damages.
Consider a retail business for example. If a supplier sends over any defective products, or products that don’t meet the safety standards, the business owners might find themselves dealing with product recalls, lawsuits, or even hefty fines. In fields like IT and healthcare, vendor audits become even more essential because if a vendor mishandles any sensitive data, it could violate the privacy laws, putting both your business and the customer information at serious risk. On the flip side, when vendors consistently deliver quality products, stick to their deadlines, and share your values, it helps build trust and makes operations run more smoothly.
It is important to understand that the vendor compliance audit isn’t just about dodging risks. It’s also about creating value. It strengthens partnerships, boosts efficiency of the supply chain management while reducing friction, and enhances your brand’s credibility.
Gain competitive edge by minimising vulnerabilities in your vendor compliance audit.
A typical vendor compliance audit involves reviewing the validity of their documents (certifications, contracts, financial records, etc.), conducting on-site or virtual inspections, interviewing key personnel, etc. The goal of vendor audits is to identify gaps, mitigate risks, and ensure clear alignments with your business goals and values.
The business environment shifts constantly. New regulations, market changes, or vendor challenges can introduce newer risks. Quarterly audits facilitate the early detection of issues like non-compliance, financial instability, or quality lapses, hence preventing any future disruptions. For example, it’s possible that a vendor cutting corners to save costs could compromise their product safety. Catching this quickly protects your business.
Laws evolve rapidly, and non-compliance can lead to hefty fines and even disrupt business operations. Quarterly audits ensure that vendors align with the latest legal standards, whether it’s labour laws, tax compliance, or environmental rules.
Regular audits pave the way for an open dialogue with vendors. By discussing the vendor audit findings and collaborating on the solutions, you not only foster accountability and trust, but also transform your vendors into reliable strategic allies.
Audits help uncovering inefficiencies like delayed deliveries or inconsistent quality, allowing you to address them promptly. This keeps your operations seamless and your customers happy.
One thing that you, as a business owner, must understand is your brand is only as strong as your vendors’ actions. Quarterly audits help you verify whether your vendors uphold ethical practices, such as fair labour or sustainable sourcing, shielding you from negative publicity.
Catching billing errors, contract violations, or quality issues early saves money. A vendor overcharging by a small margin can accumulate significant costs over time. Quarterly vendor audits prevent this.
In India, the framework around vendor compliance is shaped by a complex set of laws, varying by industry, vendor type, and sometimes the state specific regulations. Understanding these regulations is important to avoid legal trouble and ensure compliance. Here are the key laws business owners should know:
This law is mandated to ensure timely wage disbursements for all employees. The audits should check that the vendors pay their workers on time consistently and maintain transparent records.
For vendors in manufacturing or high-impact industries, compliance with pollution control and waste management rules is essential. Vendor audits should evaluate environmental clearances and sustainability practices.
Vendors handling sensitive data (e.g., IT or BPO providers) must follow data protection rules. Audits should assess their cybersecurity measures, encryption, and breach prevention protocols.
Vendors must issue compliant invoices and file accurate GST returns. Audits should verify tax compliance to prevent penalties or disputes over input tax credits.
Failing to comply with these laws can lead to fines, lawsuits, or operational halts.
Need help to ensure your vendors stay compliant and reduce your exposure to legal risks?
When a vendor supplies manpower to a principal employer, they must follow the Indian labour laws. A vendor compliance audit or supplier audit helps ensure that vendors meet their legal obligations and protect the interests of workers.
A supplier audit reviews a vendor’s documents, registrations, and processes to verify compliance with labour laws, wage payments, benefits, and employee welfare. o what exactly should you be checking? Let’s break it down.
This Act ensures workers have access to health insurance and medical benefits.
This Act mandates retirement benefits through monthly contributions.
This is a state-imposed tax deducted from employees’ drawing gross salaries of or above ₹25,000 per month.
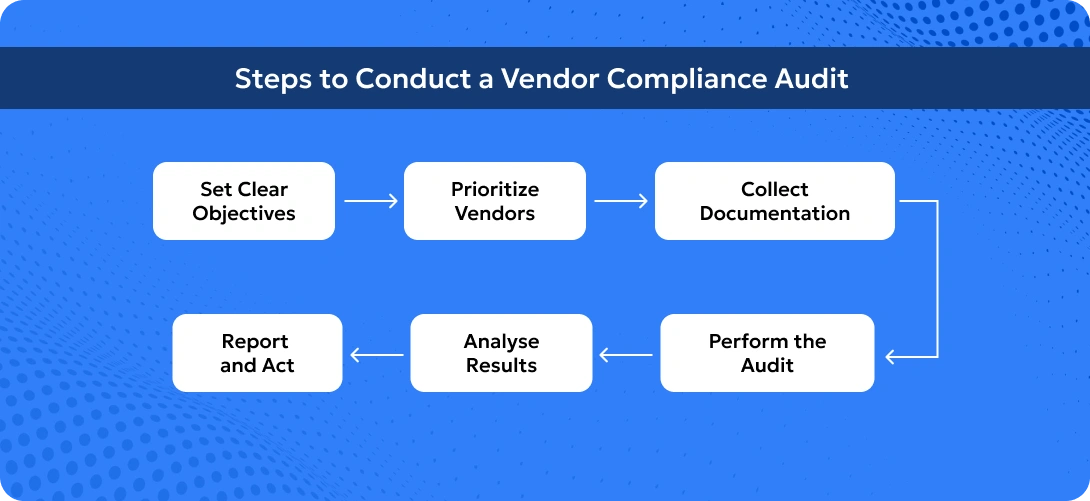
These are key checkpoints during vendor audits. Now let’s understand the steps involved in conducting a vendor compliance audit.
If you’re ready to implement quarterly audits, here’s a straightforward process to get started: